Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) can be described as autologous blood, centrifuged to remove most red blood cells, with concentrations of platelets above baseline levels, which contains at least seven growth factors and other cytokines that can stimulate healing of soft tissue and joints.
In short, blood is drawn, spun in a centrifuge, separated, activated and reinjected into a target area. For maximum effect, there are additional refinements, some of which are referred to below.
To learn more or to determine which treatment is best suited to your needs, please contact us.
PRP Composition
| Platelets |
|
| Neutrophil (PMN) |
40-75% of circulating leukocytes. |
| Monocyte macrophage |
2-10% of circulating leukocytes. Highly motile and migrate to soft tissues. |
| Fibroblasts |
produce collagen, reticular fibers, glycosaminoglycans, glycoprotein. |
| Endothelial Cell |
permeability barrier, regulate blood flow and vascular reactivity, vasodilators, vasoconstrictors, regulate inflammation and immunity. |
| Keratinocyte |
Stratified, squamous epithelial cells Primary function is to act as a barrier. |
| HSCs |
Hematopoietic stem cells (Multipotent), contain 0.06% of circulating TNCs that translate into 3-7K HSCs per ml of processed blood. |
| V-Cells |
Small Embryonic-Like Stem Cells (Pluripotent). |
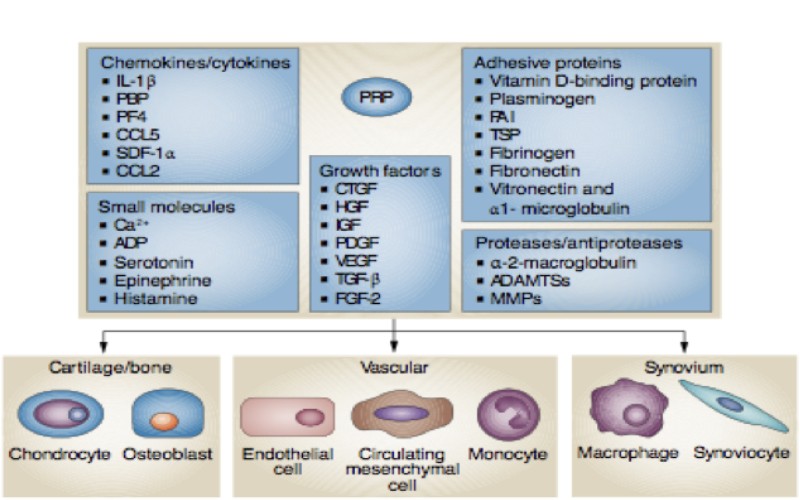
PRP Composition
Activated Platelets + Growth Factors are Critical to Recruiting Stem Cells
Platelet Activation
- Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) can be activated exogenously by thrombin, calcium chloride, or mechanical trauma. However, some newer studies show the best method of releasing these growth factors is to allow them to be released slowly when they come into contact with tissue.
- If it is activated in a more physiologic manner a tetramolecular stable network will form which enhances enmeshment of cells and growth factors.
- Tissue collagen is a strong activator of platelets.
- Employing inactivated PRP results in a more physiologic activation by the tissue into which it is injected or applied.
Photo Activated PRP Contains or Produces:
- PRP plus Autologous conditioned serum (healing and anti-inflammatory).
- Growth factors from platelets (healing)
- IL1ra and IL2ra from WBCs [white blood cells] (potent anti-inflammatory)
- Beta-endorphin from WBCs (pain relieving)
- Pro-inflammatory cytokine receptor shedding from WBCs (anti-inflammatory)
- An activated primitive stem cell in blood.
- Exosomes.
Photo activation can be done with any type of Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) but best with increased WBCs
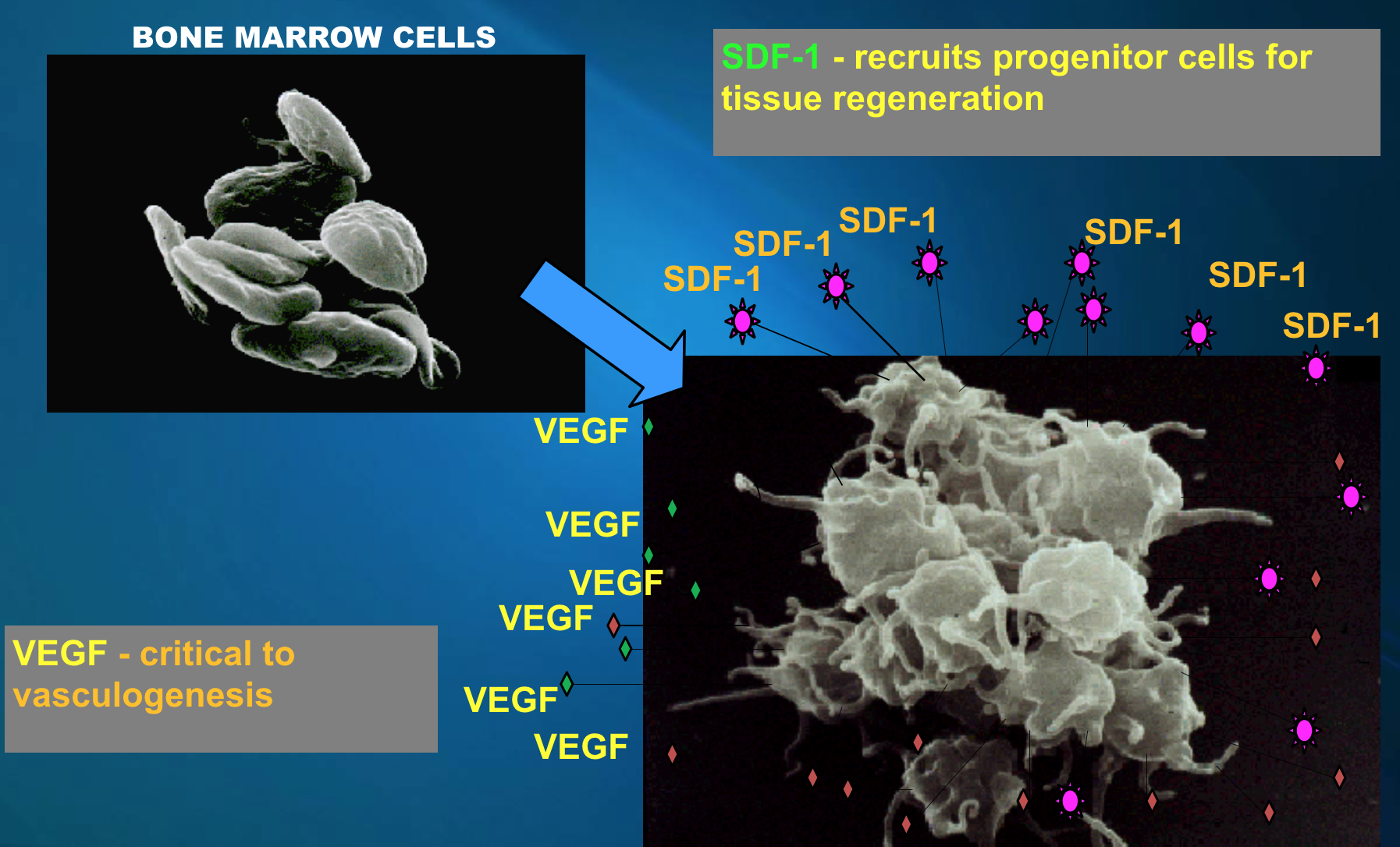
Activated Platelets are Critical to Recruiting Stem Cells
Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Growth Factors
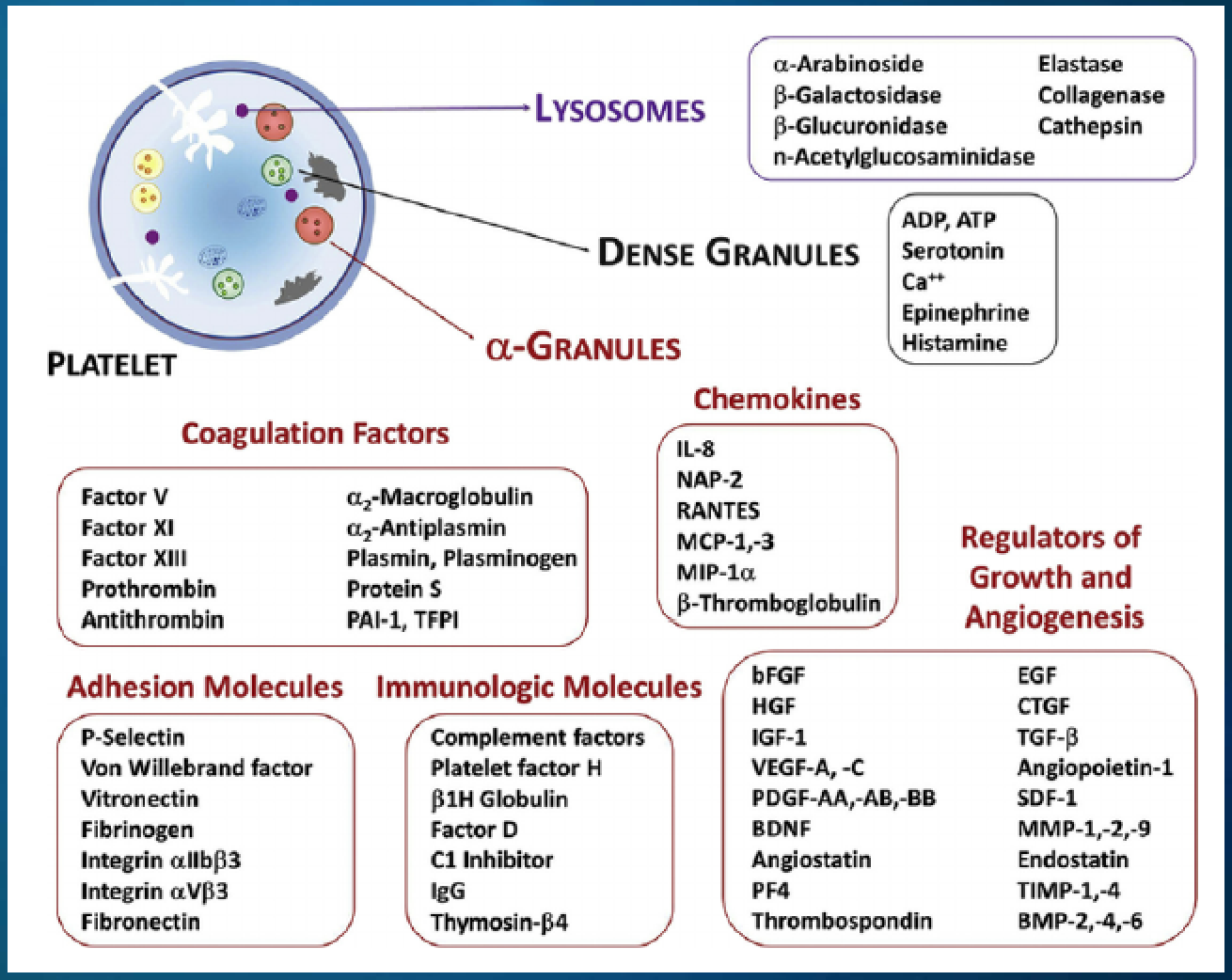
Efficacy of Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP)
The greatest potential for success may be found in Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) formulations that leverage the full array of inflammation control and wound repair mechanisms that exist in the precursor whole blood.
We are very much against a PRP product that dramatically reduces the number of white blood cells. This may cause the patient a bit less post-operative pain, simply because the PRP is not as effective.
Platelet growth factors represent only one facet of platelet bioactivity. Platelets activate inflammation that triggers wound repair in response to injury. Platelets work with RBCs and leukocytes to execute the repair process, and their cooperative engagement helps to direct the magnitude and duration of the inflammatory response.
Efficacy also depends upon the concentration and composition of components at the site of application. The optimal concentration for angiogenesis is 1.5 – 3.0 million platelets/µL, IN VITRO. Going higher than that will not increase efficacy. Indeed, platelet concentrations of 5 million platelets/µL or greater can have a negative effect.
Clinically effective PRP’s need to contain both stem cells and their homing agent. Homing is a multistep process signaled by stromal derived factor 1 alpha (SDF-1α), also called CXCL-12, stem cell factor (SCF)
The presence of very small embryonic-like stem cells (V-Cells) will make a significant difference to efficacy.
WBC’s (macrophages) are also an important element of the Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) product because they are essential for normal platelet function, including growth factor release.
Why WBCs [White Blood Cells] are important
![Why WBCs [White Blood Cells] are important Why WBCs [White Blood Cells] are important](https://www.pensummed.pro/laravel-filemanager/photos/2/5b83c39445196.png)
Depleting macrophages down regulates genes for secreting factors in nestin+ MSCs (CXCL12, ANGPT1, KITL, VCAM1) nestin MSCs lead to HSCs homing.
Macrophages affect HSC retention through regulating critical retention factors in nestin+ MSCs.
Autologous Protease Inhibitor Concentrate [APIC], also known as A2M
APIC blocks all known causes of cartilage degradation: In vitro and In vivo.
The secret behind APIC is our body’s own defense, -2-macroglobulin (A2M). This is a broad spectrum multi-purpose protease inhibitor with a high concentration in blood (up to 6 mg/ml). It inhibits MMP and ADAMTS degradation proteases. It also binds or regulates cytokines and growth factors. This just helps to illustrate the variety of inter-related elements that make up the whole complex system.
Notes:
We have used A2M and have found to date that it did not seem to give any better results than Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy.




![Why WBCs [White Blood Cells] are important Why WBCs [White Blood Cells] are important](https://www.pensummed.pro/laravel-filemanager/photos/2/5b83c39445196.png)